- Home
-
About Us
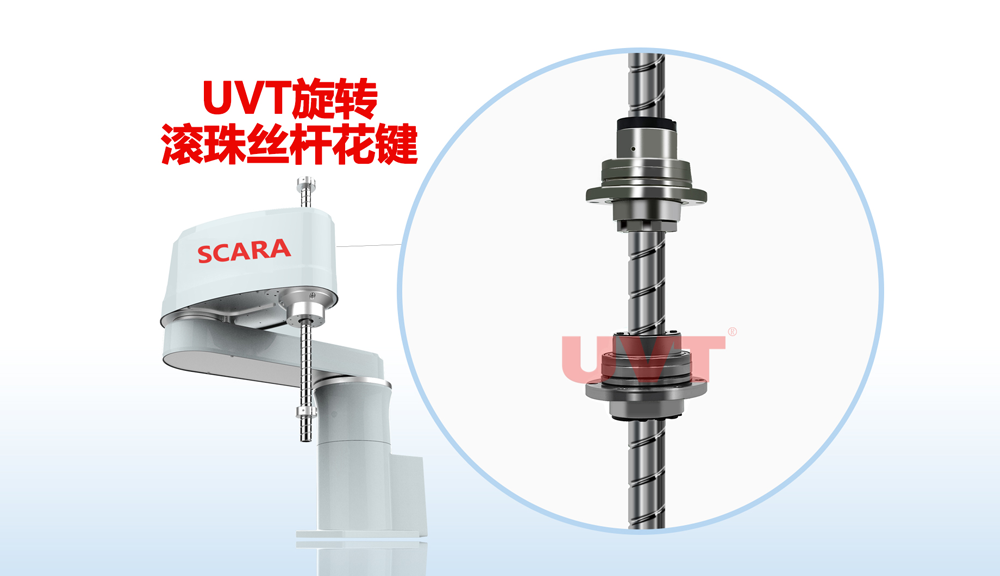
UVT products are mainly infinite stroke and limited stroke ball splines and spline rods, which are mainly used in semiconductor packaging equipment, IC test equipment, SMT mounters, AI shaped insertion machines, medical equipment, aerospace, highly inspired robots.

Customer first, continuous innovation, hard work, win-win cooperation


- Products
- Technical Support
-
News

Follow UVT to learn about the latest developments in the linear motion industry.

-
Contact Us
UVT Transmission (Dongguan) Co., Ltd.